The stock market, a complex and dynamic arena, often appears chaotic and unpredictable.
- 1. Trend Patterns: The Directional Compass
- 2. Reversal Patterns: Signalling a Shift in Momentum
- 3. Chart Patterns: Visual Representations of Market Psychology
- 4. Candlestick Patterns: Unveiling Intraday Price Action
- 5. Volume Patterns: Confirming Price Action
- 6. Timeframe Considerations: Adapting to Different Trading Styles
- 7. Combining Patterns and Indicators: Enhancing Accuracy
- Conclusion: The Art and Science of Pattern Recognition
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – Types of Patterns in the Stock Market
Yet, beneath the surface of seemingly random price fluctuations, a world of discernible patterns lies. These patterns can provide valuable insights into market sentiment, potential price movements, and strategic trading opportunities when understood and interpreted.
This exploration delves into the various patterns observed in the stock market, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate its intricate landscape.
1. Trend Patterns: The Directional Compass
Trend patterns reveal the prevailing direction of price movement, offering clues about the market’s overall sentiment and potential future trajectory.
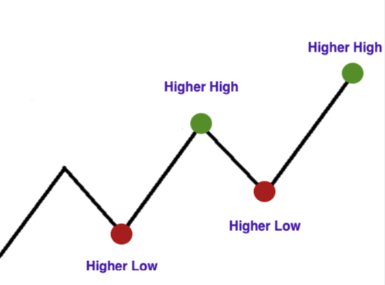
- Uptrends: Characterized by a series of higher highs and higher lows, uptrends signify a bullish market in which demand outweighs supply.

We see continuation patterns within uptrends, suggesting the trend is likely to persist.
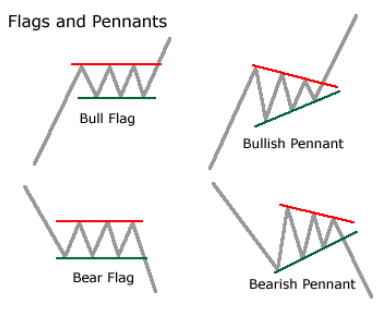
- Flags and Pennants: These short-term patterns resemble small rectangles or triangles, indicating a brief consolidation period before the uptrend resumes.

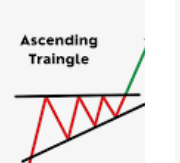
- Ascending Triangles: This pattern features a horizontal resistance line and an ascending support line, suggesting increasing buying pressure.

- Downtrends: Defined by a series of lower highs and lower lows, downtrends indicate a bearish market in which supply exceeds demand.
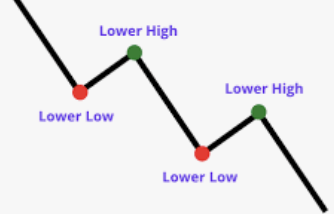

Similar to uptrends, downtrends also exhibit continuation patterns.
- Flags and Pennants: When observed in a downtrend, these patterns signal a continuation of the bearish momentum.
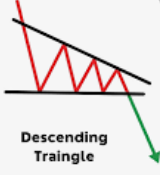
- Descending Triangles: This pattern features a horizontal support line and a descending resistance line, indicating increasing selling pressure.

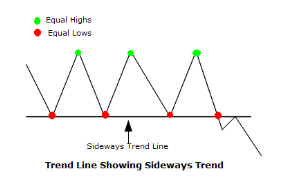
- Sideways Trends (Consolidation): When prices move within a horizontal range, forming neither higher highs nor lower lows, it signifies a sideways trend or consolidation phase.

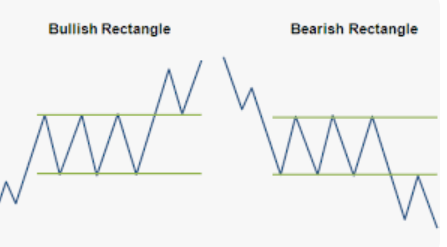
- Rectangles: These patterns represent a period of equilibrium between buyers and sellers, with prices fluctuating within a defined range.

2. Reversal Patterns: Signalling a Shift in Momentum
Reversal patterns indicate a potential change in the prevailing trend, suggesting a shift in market sentiment and a possible price reversal.
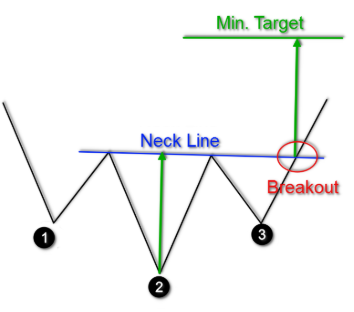
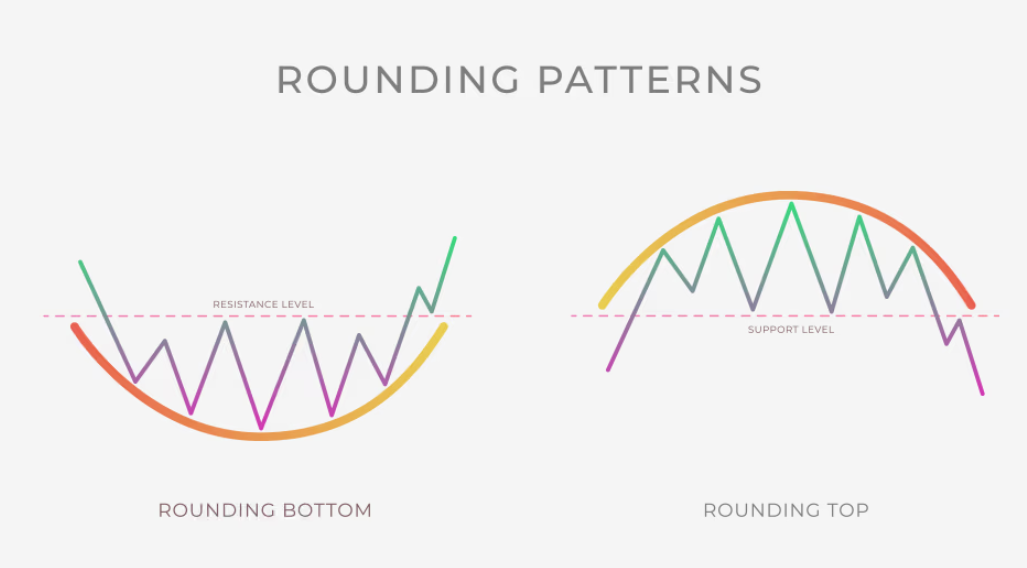
- Head and Shoulders: This pattern, resembling a human head with two shoulders, signals a potential reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend. The “head” represents the highest high, and the “shoulders” are lower highs on either side.
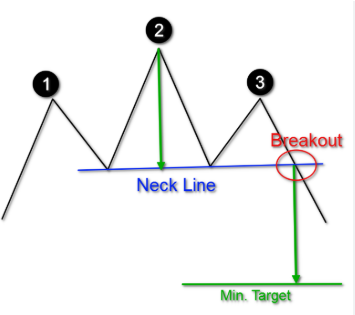

- Inverse Head and Shoulders: The opposite of the head and shoulders pattern, this pattern signals a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.

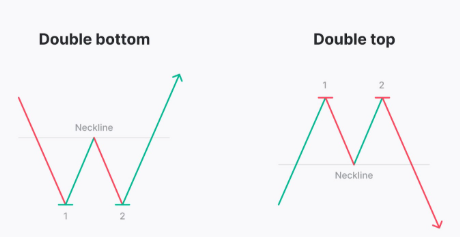
- Double Tops and Bottoms: These patterns feature two consecutive peaks or troughs at roughly the same price level, indicating that the current trend has failed to continue.
- Double Top: This signifies a potential reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend.
- Double Bottom: This signifies a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.

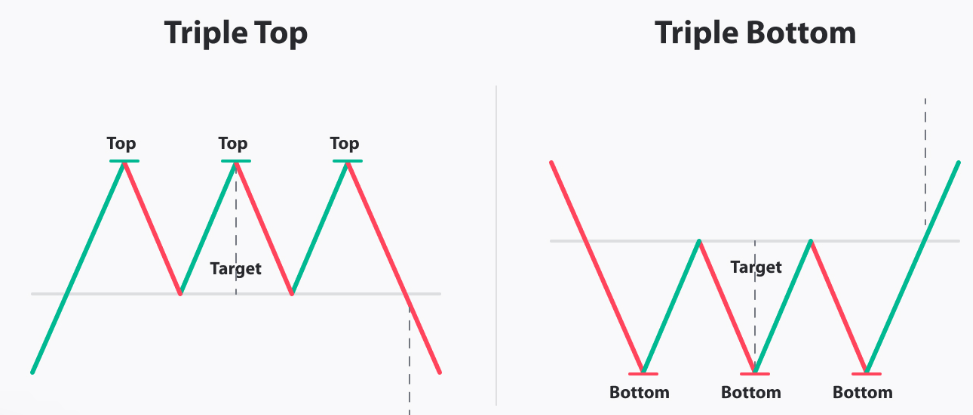
- Triple Tops and Bottoms: Similar to double tops and bottoms, these patterns feature three consecutive peaks or troughs, further strengthening the reversal signal.

- Rounding Tops and Bottoms: These patterns, resembling a gradual curve, indicate a slow and steady reversal of the prevailing trend.

3. Chart Patterns: Visual Representations of Market Psychology
Chart patterns, formed by the price action on a stock chart, provide visual representations of market psychology and potential future price movements.
- Triangles: These patterns, formed by converging trendlines, indicate a period of consolidation before a potential breakout.
- Symmetrical Triangles: These patterns feature converging trendlines with similar slopes, indicating a period of indecision before a potential breakout in either direction.
- Ascending Triangles: As mentioned earlier, these patterns indicate increasing buying pressure and a potential breakout to the upside.
- Descending Triangles: As mentioned earlier, these patterns indicate increasing selling pressure and a potential breakout to the downside.
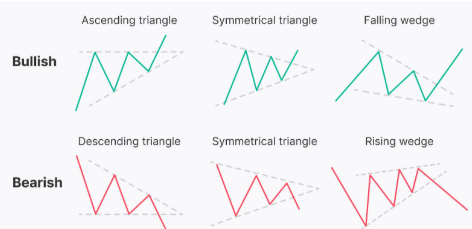

- Wedges: These patterns, formed by converging trendlines that slope in the same direction, indicate a potential reversal of the prevailing trend.
- Rising Wedges: These patterns indicate a potential reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend.
- Falling Wedges: These patterns indicate a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.
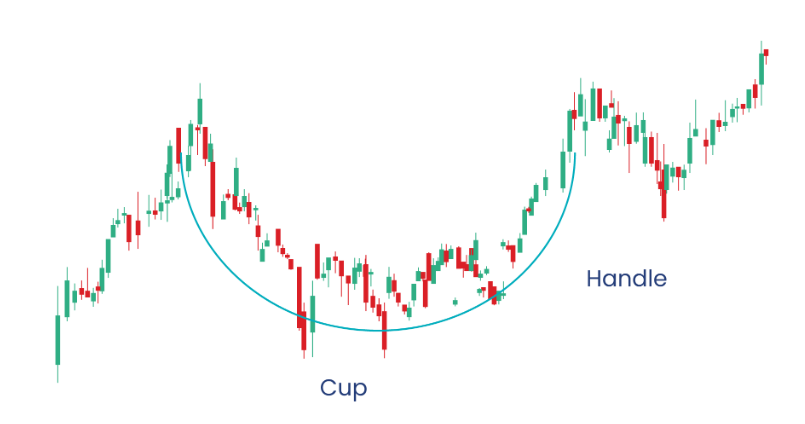
- Cup and Handle: This bullish continuation pattern resembles a cup with a handle. It indicates a period of consolidation after an uptrend, followed by a potential breakout to the upside.

- Flags and Pennants: As previously discussed, these short-term patterns indicate a brief consolidation period before the prevailing trend resumes.
4. Candlestick Patterns: Unveiling Intraday Price Action
Candlestick patterns, formed by a stock’s open, high, low, and close prices within a specific period, provide insights into intraday price action and potential short-term price movements.
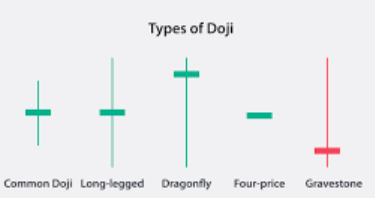
- Doji: This pattern, characterised by a small body and long upper and lower shadows, indicates indecision in the market.

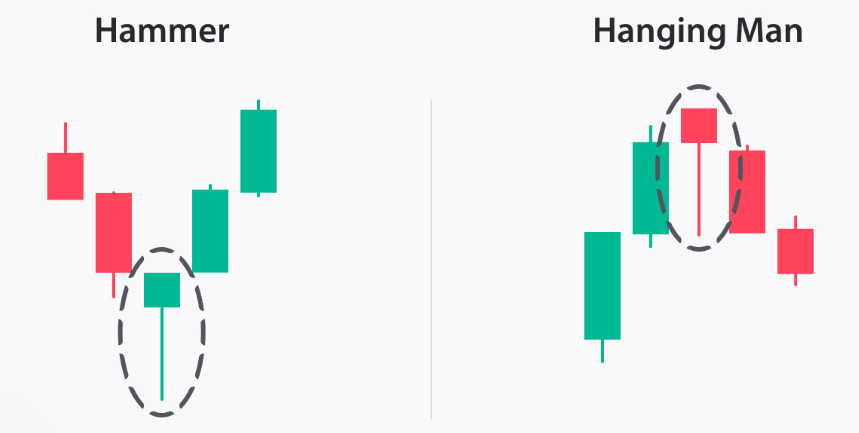
- Hammer and Hanging Man: These patterns, resembling a hammer or a hanging man, indicate a potential reversal of the prevailing trend.
- Hammer: Indicates a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.
- Hanging Man: Indicates a potential reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend.

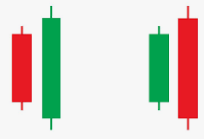
- Engulfing Patterns: These patterns, consisting of two candlesticks, indicate a potential reversal of the prevailing trend.
- Bullish Engulfing: Indicates a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.
- Bearish Engulfing: Indicates a potential reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend.

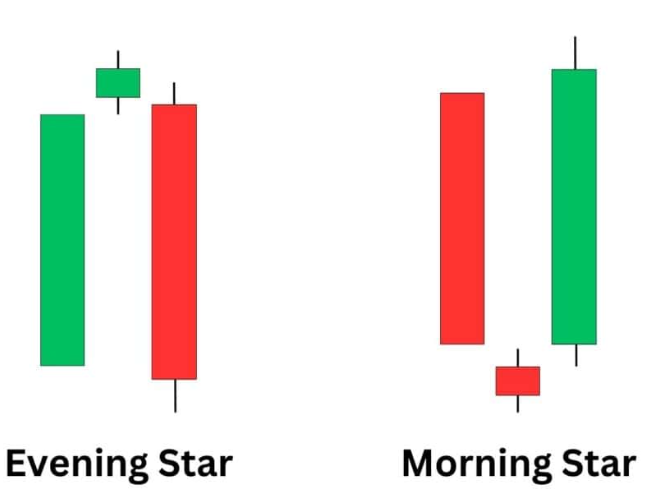
- Morning Star and Evening Star: These three candlestick patterns indicate a potential reversal of the prevailing trend.
- Morning Star: Indicates a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.
- Evening Star: Indicates a potential reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend.

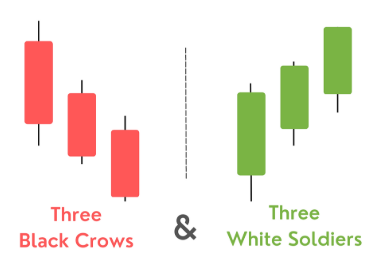
- Three White Soldiers and Three Black Crows: These patterns, consisting of three consecutive bullish or bearish candlesticks, indicate a potential continuation of the prevailing trend.
- Three White Soldiers: Indicates a potential continuation of an uptrend.
- Three Black Crows: Indicates a potential continuation of a downtrend.

5. Volume Patterns: Confirming Price Action
Volume patterns provide insights into the strength and validity of price movements, confirming or contradicting the signals generated by other patterns.
- Volume Confirmation: Increasing volume during a price breakout or trend continuation strengthens the signal, indicating strong buying or selling pressure.
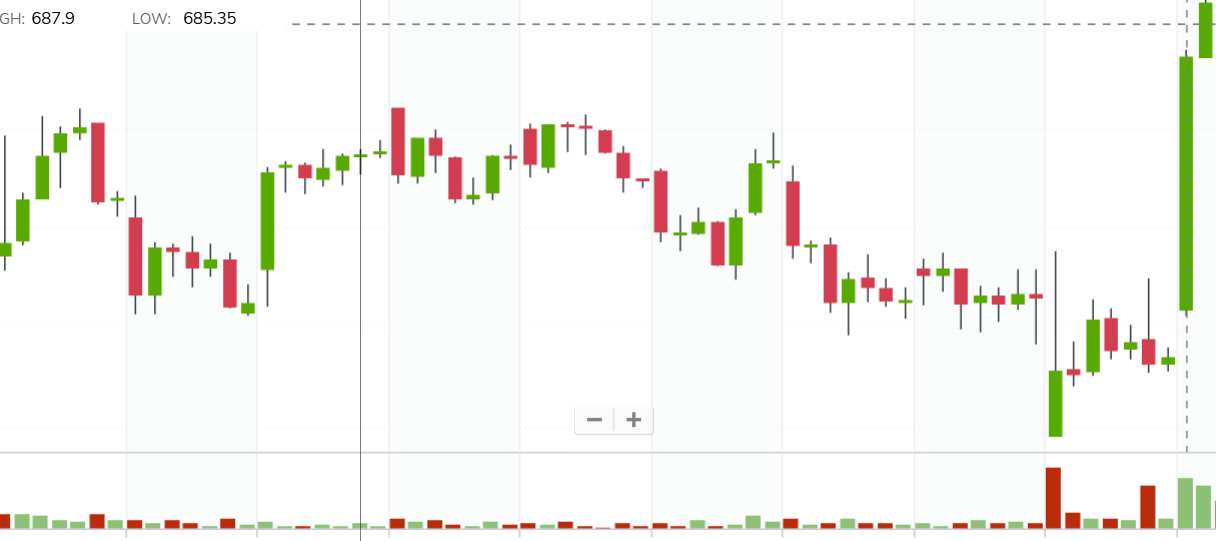

- Volume Divergence: Divergence between price and volume, such as prices rising on decreasing volume, suggests a potential weakening of the trend and a possible reversal.

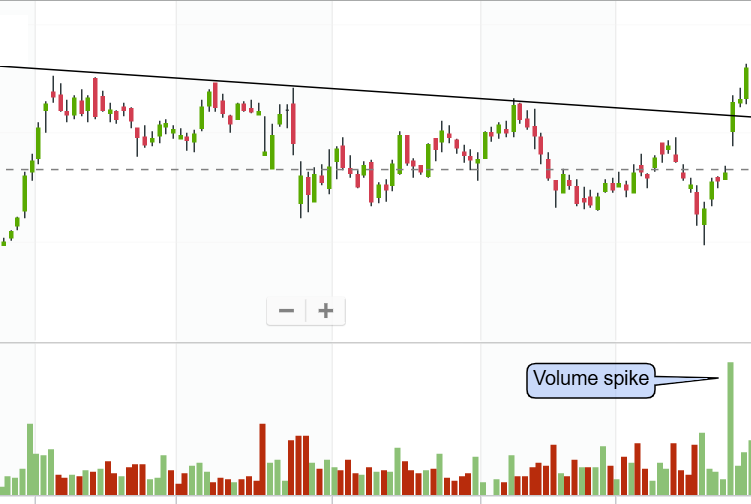
- Volume Spikes: Sudden and significant increases in volume can indicate significant market events or shifts in sentiment.

6. Timeframe Considerations: Adapting to Different Trading Styles
The relevance and significance of patterns can vary depending on the timeframe being analysed.
- Short-Term Patterns: Intraday and daily charts identify short-term patterns suitable for day traders and scalpers.
- Medium-Term Patterns: Weekly and monthly charts are used to identify medium-term patterns suitable for swing and position traders.
- Long-Term Patterns: Monthly and yearly charts are used to identify long-term patterns suitable for long-term investors.
7. Combining Patterns and Indicators: Enhancing Accuracy
Combining pattern analysis with technical indicators, such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and moving average convergence divergence (MACD),1 can enhance the accuracy of trading signals and provide a more comprehensive view of the market.
Conclusion: The Art and Science of Pattern Recognition
Pattern recognition in the stock market is both an art and a science. It requires a keen eye for detail, a deep understanding of market psychology, and a disciplined approach to analysis.
By mastering the various patterns discussed in this exploration, you can gain a significant edge in navigating the complexities of the stock market, making more informed trading decisions, and enhancing your potential for success.
Remember, patterns are not foolproof predictors of future price movements, but they can provide valuable insights and increase your probability of making profitable trades. Continuous learning, practice, and adaptation are essential for mastering the art of pattern recognition and achieving consistent success in the dynamic world of the stock market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – Types of Patterns in the Stock Market
Q: What are stock market patterns, and why are they important?
A: Stock market patterns are recurring formations in price charts that traders use to predict future price movements. They’re important because they reflect market psychology and can provide valuable trading signals.
Q: What are trend patterns, and what types exist?
A: Trend patterns show the direction of price movement. Types include uptrends (higher highs and lows), downtrends (lower highs and lows), and sideways trends (consolidation within a range).
Q: What are continuation patterns, and how do they differ from reversal patterns?
A: Continuation patterns signal that the current trend will likely continue (like flags and pennants). Reversal patterns indicate a potential change in the trend (like head and shoulders).
Q: What are reversal patterns, and what are some common examples?
A: Reversal patterns suggest a change in the current trend. Examples include head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, and rounding tops/bottoms.
Q: What is a Head and Shoulders pattern, and what does it indicate?
A: A Head and Shoulders pattern resembles a human head with two shoulders and signals a potential reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend.
Q: What are chart patterns, and how are they formed?
A: Chart patterns are visual representations of price movements on a stock chart, formed by converging trendlines and price action.
Q: What are triangles in chart patterns, and what types exist?
A: Triangles are formed by converging trendlines, indicating consolidation before a potential breakout. Types include symmetrical, ascending, and descending triangles.
Q: What are wedges in chart patterns, and what do they indicate?
A: Wedges are formed by converging trendlines that slope in the same direction, indicating a potential trend reversal. Rising wedges suggest a downtrend reversal, and falling wedges an uptrend.
Q: What is a Cup and Handle pattern, and what does it suggest?
A: A Cup and Handle is a bullish continuation pattern, suggesting a period of consolidation followed by a potential upward breakout.
Q: What are candlestick patterns, and what information do they provide?
A: Candlestick patterns represent price action within a specific period, providing insights into intraday price movements and potential short-term trends.
Q: What is a Doji candlestick, and what does it indicate?
A: A Doji has a small body and long shadows, indicating indecision in the market.
Q: What do Hammer and Hanging Man candlestick patterns indicate?
A: A Hammer signals a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend, while a Hanging Man signals a possible reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend.
Q: What are engulfing patterns, and what are the bullish and bearish variations?
A: Engulfing patterns consist of two candlesticks, indicating a potential reversal. Bullish engulfing signals a potential uptrend, and bearish engulfing is a possible downtrend.
Q: What are Morning Star and Evening Star patterns, and what do they suggest?
A: These three candlestick patterns indicate potential trend reversals. Morning Star suggests an uptrend, and Evening Star a downtrend.
Q: How does volume analysis help in confirming patterns?
A: Volume analysis confirms the strength of price movements. Increasing volume during breakouts strengthens signals, while volume divergence weakens them.
Q: How does timeframe analysis impact pattern interpretation?
A: Short-term patterns are for day traders, medium-term for swing traders, and long-term for investors. The significance of patterns varies with the timeframe.
Q: How can technical indicators be used with patterns?
A: Technical indicators like moving averages, RSI, and MACD can confirm pattern signals and provide a more comprehensive market view.
Q: Are patterns foolproof predictors of market movements?
A: No, patterns are not foolproof. They provide insights and probabilities, but market conditions can change rapidly.
Q: How can I improve my pattern recognition skills?
A: Practice with charts, study different patterns and combine pattern analysis with other technical tools. Continuous learning and experience are key.
Q: What is the benefit of learning stock market patterns?
A: Learning patterns can help you make more informed trading decisions, spot potential opportunities, and manage risk more effectively.
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing. This content is purely for educational purposes only and in no way to be considered as advice or recommendation. The securities are quoted as an example and not as a recommendation. Paytm Money Ltd SEBI Reg No. Broking – INZ000240532, Depository Participant – IN – DP – 416 – 2019, Depository Participant Number: CDSL – 12088800, NSE (90165), BSE (6707), Regd Office: 136, 1st Floor, Devika Tower, Nehru Place, Delhi – 110019. For complete. Terms & Conditions and Disclaimers visit: https://www.paytmmoney.com/stocks/policies/terms.