Hedging Using Futures & Options5 min read
What Is Hedging?
A hedge is an investment done with the goal of reducing the risk of adverse price movements in an asset. A hedge is an investment in a security that correlates well with the asset to be hedged.
How Does Hedging Work?
Hedging is an effective tool that provides protection against downside risk in times of uncertainty. The most common hedge is the famous 60/40 stock and bond portfolio held by retirement savers. Every kind of diversification is a hedge in a way. That is why a portfolio of 20 – 21 stocks is considered a safer investment than just investing in 2 stocks like Reliance and Bharti Airtel.
Examples Of Hedging:
1. Hedging a single stock position using Futures: Let us assume that you are long 300 stocks of SBIN at Rs. 420. This is a total investment of Rs. 1,26,000. Now you are uncertain about the SBIN stock’s near future. So you decide to hedge this exposure using the futures market. The lot size is 300 and the futures price is Rs. 421. Since you are long the stocks, you decide to short the futures market by selling 1 lot of futures. This will be an amount worth Rs. 1,26,300. Now the additional 300 will be extra as one can never achieve a perfect hedge. And if the price moves around, the hedge will be acting like a protection for the actual stock position.
2. Commodity Futures: Companies in the airline industry are dependent on the prices of fuel. When the price of oil goes up, one of the input costs for the airline company goes up. That reduces the stock price. So an investor holding airline stocks can hedge his exposure by buying oil futures. When the price of oil goes up, the airline stock declines but at the same time oil futures would have appreciated. This how the oil hedge works perfectly for an airline stock.
3. Diversification: Diversification is the most famous form of hedging non-systematic risk. If we buy a number of stocks for our portfolio, then the idiosyncratic risk is reduced. Let us say that we hold technology and banking stocks in our portfolio, then if the technology stocks decline then the banking stocks can act as a hedge.
4. Stock Portfolio hedge with Index Futures: Let us first learn about the two types of risks – systematic and non-systematic risks. When we diversify a portfolio of stocks, we are reducing the idiosyncratic risk i.e. the non-systematic risk. To reduce the macro/market risk i.e. the systematic risk, we need to make use of an index future that kind of replicates the market movements. The table below shows our portfolio of stocks.
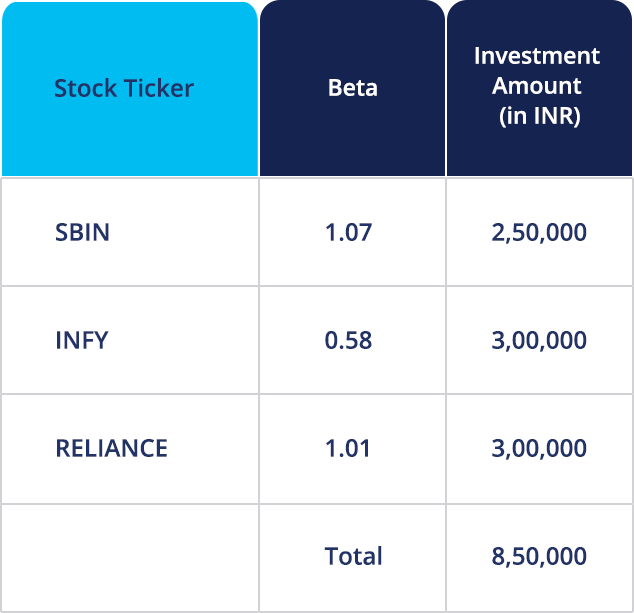
Now to calculate overall portfolio beta, we need to calculate the weightage associated with the beta of each stock.
Weightage of SBIN = Rs. 2,50,000/Rs. 8,50,000 = 0.294
Weightage of INFY = Rs. 3,00,000/Rs. 8,50,000 = 0.352
Weightage of RELIANCE = Rs. 3,00,000/Rs. 8,50,000 = 0.352
Overall portfolio beta = (0.294*1.07) + (0.352*0.58) + (0.352*1.01) = 0.87426
Now, we need to calculate the hedge value which is simply the product of overall portfolio beta and total investment.
Hedge Value = 0.87426* Rs. 8,50,000 = Rs. 7,43,121.
Let us use Nifty futures to hedge the stock portfolio. Nifty futures is currently trading at 15,727 and the lot size is 50.
So the contract value per lot is Rs. 7,86,350.
Hence the number of lots required to short the Nifty futures would be Rs. 7,43,121/ Rs. 7,86,350 = 0.945.
As already explained, we can never have a perfect hedge. In this case, if we short 1 lot of Nifty futures contract, then we will be over-hedged and if we do not short any lots, then we will be under-hedged.
5. Covered Call Options: A covered call is when you buy a stock and write a call option on the same stock simultaneously. If you have bought stock X with the goal of long-term price appreciation, then the stock can have a flat trading period where the stock moves around within a defined price range. In this case, you can sell options on the stock to earn income while the stock moves around within the price range.
Benefits Of Hedging
1. A hedge can protect your capital in the case of a black swan event. A black swan event is something that occurs rarely but has the potential to cause massive destruction of wealth in the financial markets. A hedge can simply keep you in the business when things go from bad to catastrophic. In March 2020, almost all asset classes dipped as investors faced a liquidity crunch. However, there were some trades in the interest rate market like interest rate swaps that acted as very good hedges for the equity downfall.
2. Traders and investors with a low tolerance for risk can use a hedge to preserve not only capital but also achieve peace of mind. By putting on a hedge, traders and investors can make consistent gains while also have peace of mind by knowing that they are not taking too much risk.
Drawbacks Of Hedging
1. Hedging provides muted returns as it eats away from your return stream. A hedge is useful only if you expect a sudden spike in volatility. If you expect the returns to go up higher, then a hedge will only be a drag on your portfolio performance.
2. Hedging involves buying a financial asset to offset the risk of another. The purchase of financial assets come with transaction costs. If the trade for the hedge is not well planned and executed, it can end up eating away your returns by incurring heavy transaction costs.
Disclaimer –
This content is purely for information and investor awareness purpose only and in no way an advice or recommendation. You should independently research and verify the information you find on our website/application. The securities quoted are exemplary and are not recommendatory. Investment in securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing. Paytm Money Ltd SEBI Reg No. Broking – INZ000240532. NSE (90165), BSE(6707) Regd Office: 136, 1st Floor, Devika Tower, Nehru Place, Delhi – 110019